Do you have an e-commerce website that you’d like to optimize for Google search? Or do you run a digital agency that caters to these types of businesses? If so, then this ultimate SEO for ecommerce guide is for you.
As of 2022, there are an estimated 24 Million e-commerce sites on the planet, and more are created everyday. However, only less than 1 million of these sites earn at least $1,000 each month.
So what separates the profitable online stores from those that don’t make money?
Two things: Traffic and visibility.
And both can be had through search engine optimization (SEO):
What Is SEO For Ecommerce?
The simplest definition is this:
SEO For Ecommerce is the art or process of performing search engine optimization on an e-commerce site to make it more visible on the Google search platform.
An e-commerce website is any website that sells tangible products to a specific market. Usually it is represented by an online store that features dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of product listings.
The business typically makes money when customers order products through an online checkout process. The payment is then processed and the order is shipped to the buyer.
Sounds simple? Not really.
Before buyers can purchase your products, first they need to FIND your online store.
This is where SEO (search engine optimization) comes in.
Why Perform SEO for Ecommerce Websites?
According to recent stats by Reboot Online, Google search is the source of approximately 43% of all e-commerce traffic generated on the web.
But this applies mainly to businesses that have done a fair bit of SEO on their sites.
So if you aren’t using best ecommerce SEO practices, chances are you’re missing out on a huge chunk of potential traffic and sales!
Some store owners rely mainly on advertising to keep their business afloat.
But with the fierce competition nowadays in advertising platforms such as Facebook and Google Ads, implementing a long term, profitable advertising campaign can be a steep challenge.
So never rely on just advertising to promote your online store.
Instead, use proven SEO strategies to position your business in front of thousands of potential buyers on the web – without spending a dime on advertising!
But how can you perform SEO for an e-commerce website?
Here are the steps:
Set Proper Ecommerce SEO Architecture and Optimize Your Main Pages
Note, this blog post will NOT cover the basics of search engine optimization, but rather, we will tackle the basics of performing SEO specifically for e-commerce. (If you run a service based business or B2B website, we will tackle that in another post).
The first question that online store owners ask is “where do I start”. Just to give you an overview, start with these three important things:
1. Optimize the homepage
Your first priority is optimizing the homepage for Google search.
In a nutshell, this can be done by doing the following:
- Research one (1) main focus keyword for the homepage and around 3-5 secondary phrases. Ideally, the keywords should be main industry phrases in your niche, such as “outdoor gear”, “scented candles” or “power tools”.
- You can further drill down these keywords by adding modifiers such as location (country wide “Australia”, city wide “Toronto”, or town/suburb such as “St. Peters”).
- Once you have these keywords, implement them strategically on your page through the meta tags, image tags, headings, content, and URL.
2. Optimize the product category and subcategory pages
Product category and subcategory pages are very important for your e-commerce website. You have lots of opportunity to target very specific terms in those pages. Follow these steps:
- Drill down into the types of products you offer. For example, if you have an outdoor gear website, you can target several types of outdoor gear in the product category pages: backpacks, camping equipment, outdoor shoes, mountain climbing gear, etc.
- Assign a clear keyword theme on each product category and subcategory page. In your keyword research, ensure that each page will only have one (1) focus keyword and around 3-5 secondary keywords. You don’t want to have category pages that are too similar to each other in terms of keyword targeting, or else they will compete with each other on Google search.
- Implement the keywords strategically on each page. Same thing as the homepage. Your keywords should be implemented strategically on your site’s meta tags, URL, post title, headings. image tags, and other areas.
3. Optimize the product pages
This is what will take the most of time, depending on the number of products you have in your catalog.
If you have hundreds of product pages, use the unique and exact product name in the meta tags, image tags, main heading (H1), URL and other on-page areas.
The key thing to remember is to make each product page unique in the eyes of the search engines. So make an effort to differentiate very similar product models by using modifiers such as SKU, color, size, and specs within the on-page elements.
4. Optimize your blog posts
Create blog topics that target specific keywords not yet covered in the homepage, category pages, subcategory pages, and product pages.
For blog posts, try to research and target keywords that are information-based instead of transactional. “How to” guides work best. You may also publish listicles and roundups such as “Top 25 Mountain Climbing Gear”, or any relevant list article relevant to your niche.
You can use blog posts as a springboard to link towards relevant pages on your site where people can make a purchase (also known as “money pages”).
As you publish more high quality, keyword targeted and SEO-friendly blogs, you’ll see a a bump in your traffic over time. In turn, this could increase your traffic and sales.
Apply Ecommerce SEO Best Practices
Now let’s discuss some more specific SEO steps:
Keyword research for online stores
Your goal in this step is to uncover keyword themes to use for each essential page on your site. This process can be semi-automated, but in my experience, the best outcomes can be achieved if you do it manually, by hand (with the help of SEO tools of course).
You can easily do this by using a keyword research tool such as Ubersuggest. For example if you have an e-commerce website that sells “swim wear”, you can use that phrase as a seed keyword to uncover other possible phrases to target.
Go to your keyword tool, input that seed keyword in the keyword suggestion box, set the target country, and click on “Search”:
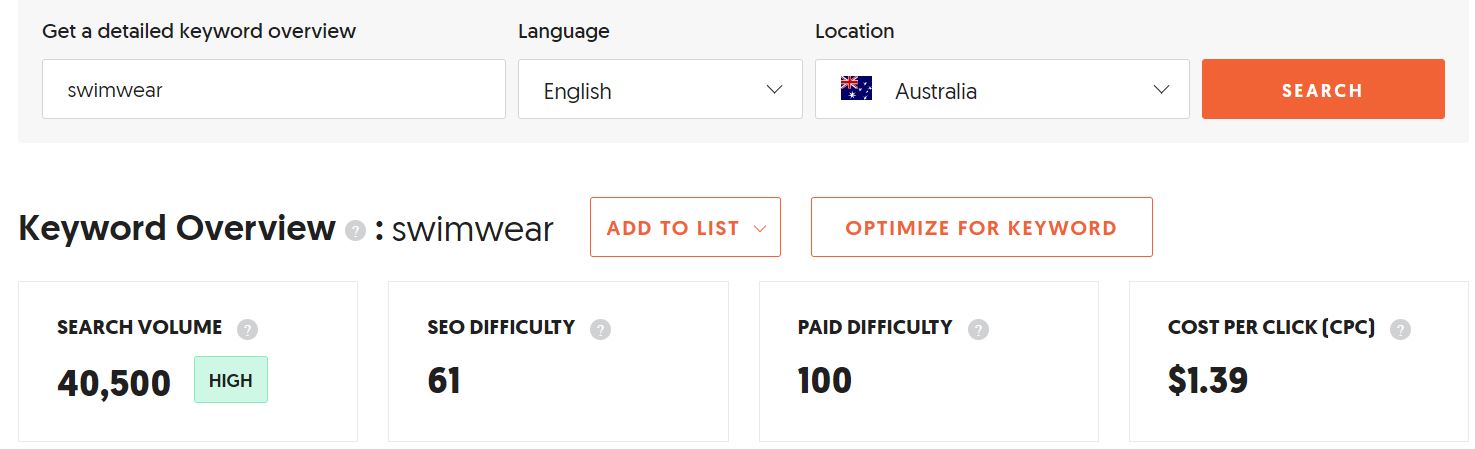
As you can see, there are over 40,000+ searches for this keyword phrase every month within Australia. However, the SEO difficulty is quite high at 61. It means the keyword has lots of competition.
If you think your brand or website authority can handle the high level of competition for this keyword, you may stop looking for a main focus keyword and just use “swimwear”.
However, in most cases, it would be fairly difficult to rank for such a competitive term. So here’s what you can do:
Add a modifier.
A modifier is something you add to your seed keyword to further drill it down and make it specific.
In an ecommerce website, the best modifier to add is a “country modifier”, in which you use the term “swim wear + targeted country” for the home page.
So using that example again, let’s run the keyword tool again:
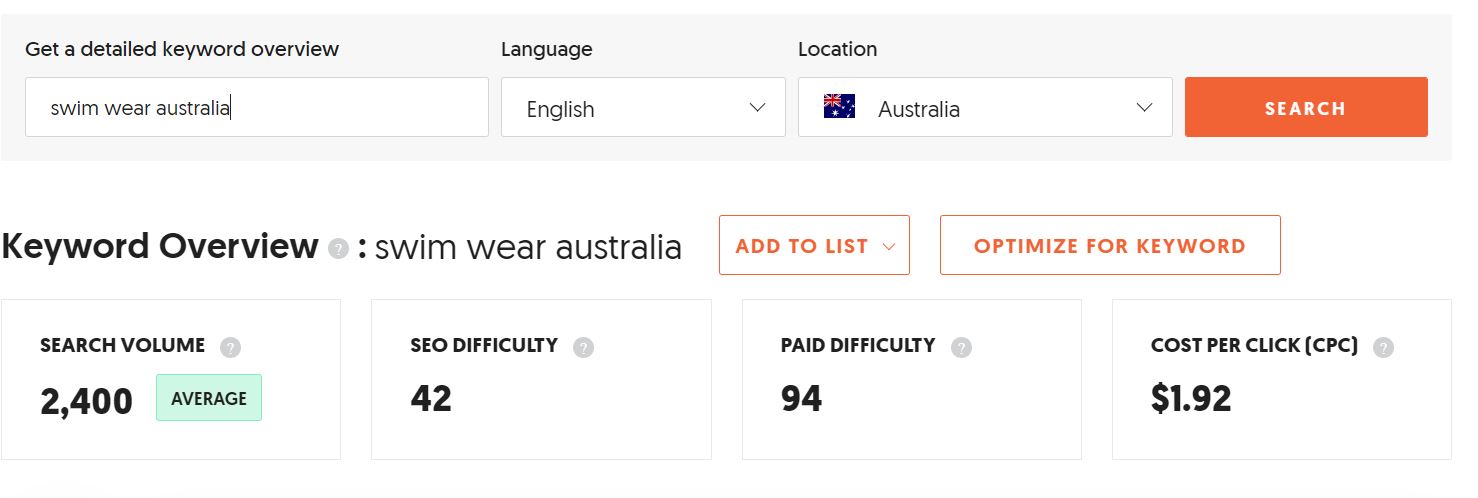
As you can see, just by adding a modifier, we are able to find a keyword with respectable search volume but with a lower SEO difficulty. Depends on whether this keyword is highly relevant to what you’re selling, you can make a judgment call to choose this phrase as your focus keyword for the homepage.
There are other modifiers you can try:
- Town or city
- Gender (swimwear for men, swimwear for women, unisex swimwear, etc)
- Age group (swim wear for kids, swim wear for adults, swim wear for seniors)
- and many others!
To research secondary keywords you can target for the homepage, just scroll down to your SEO tool and see the other keyword suggestions:
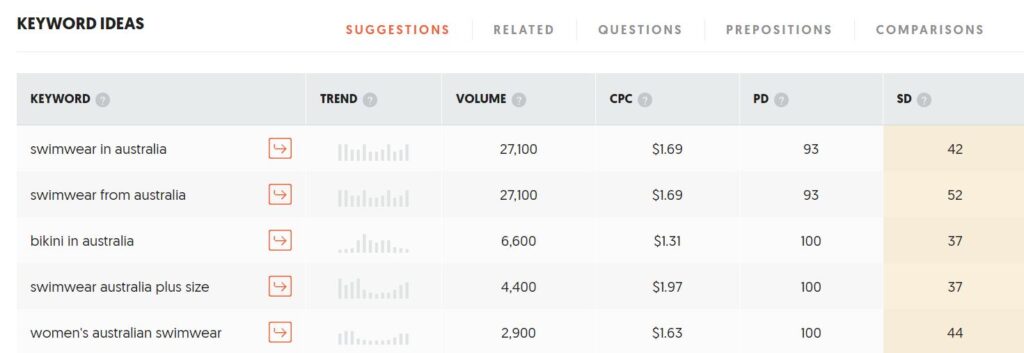
It’s possible to uncover dozens or even hundreds of phrases based on your initial seed keyword. Choose 3-5 keywords that are most relevant to the page you are optimizing, has a decent search volume, and manageable search difficulty (any SD rating of around 10 to 40 means the competition is moderate, while higher numbers indicate high competition for any given keyword).
Once you pick the keywords you will use for your homepage, do the same thing for your category pages, subcategories, and product pages.
To manage this process in a more organized way, do this:
Keyword mapping for ecommerce
It may be tough to remember all the keywords you researched and assigned to each page on your site. So the solution to organize all of this is to perform a “keyword mapping” exercise.
A keyword map lists down ALL the pages on your e-commerce site that you’d like to optimize for search. Then, it also lists down the following information:
- Focus keyword for each landing page
- Search volume for focus keyword
- Secondary keywords for each page
- Meta titles and descriptions to be used on each page (should adhere to recommended Google guidelines – 50 to 65 chars for title tag, and around 140-150 chars for meta description),
- H1 tag to be used for each page
This means, you will have to map out everything on Excel or Google Spreadsheets before you even implement them on your site.
A keyword map looks like this:
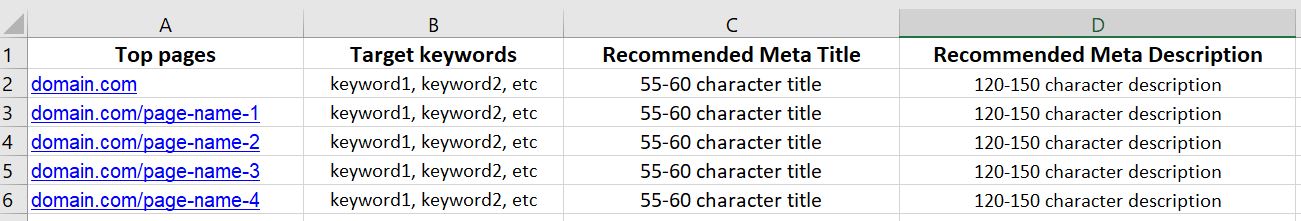
Once you’ve finished your keyword map, it’s time to implement them on your site. Here’s the next step:
Perform on-page SEO implementation on your ecommerce site
This is the part where you implement all the info in your keyword map into your actual site.
On-page implementation is actually the easier part of SEO, but unfortunately, a lot of people do it wrong.
So here’s what to do:
- If your site is in WordPress, download and install the free plugin called “Yoast SEO“. Chances are, you are already familiar with this tool. But in case not, it is a tool that allows you to manually or automatically modify the meta title tag, meta description, and other on-page elements of your site.
- After you have downloaded and installed Yoast on your site, go to “Edit” mode for each of the pages or posts that you’d like to optimize. Input the title tags and descriptions you wrote in your keyword and then hit “Publish” or “Update”.
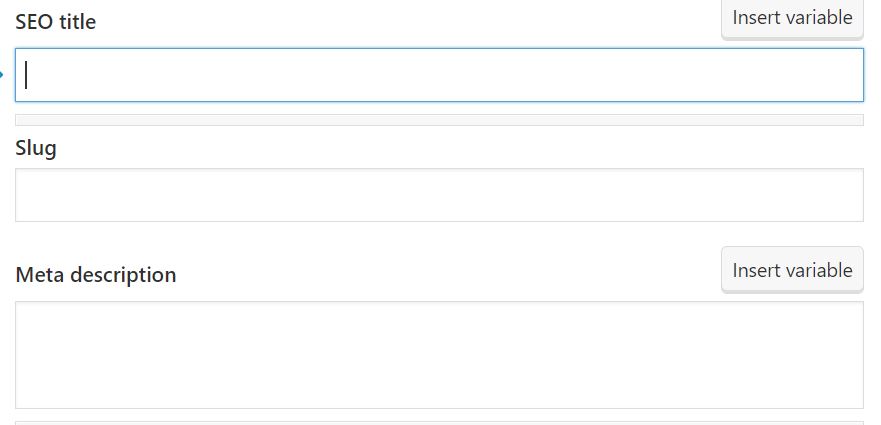
- For WordPress sites, the heading title of your post or page usually becomes the H1 tag. So make sure that your main page heading targets your main keyword naturally for search, but also makes sense for the readers. For the homepage, you may need to place a custom H1 heading.
- Implement your main target keyword on the image alt tags.
- Implement your 3-5 secondary keywords naturally within the body of the content, and into the H2, H3 and H4 headings.
- Do this for each page you are optimizing!
Sounds like a lot of work? Yeah, it really is. But it’s all worth it.
If your site is not built on WordPress, the above steps for implementation may vary a little bit. Some CMS platforms, such as Magento and Shopify, allow you to directly input your title tags on each page without downloading any plugin such as Yoast. So check the functions of your CMS and work your way from there.
Resolve Common SEO Errors on your Ecommerce Website

E-commerce websites are prone to several types of SEO errors. It’s important to stay on the look out for these errors so you can fix them accordingly. This ensures that your site is always squeaky clean, search engine friendly, and has a smooth user experience.
First, you need to detect the SEO errors on your site as they arise. A lot of e-commerce site owners don’t do this. By the time they discover the technical errors, it has already snowballed to thousands of issues and very hard to resolve.
Follow these steps:
Perform a monthly technical audit for your e-commerce store
A technical audit is done by using any enterprise SEO tool to crawl your website and detect any errors. It is very important to do this at least once per month, especially for e-commerce sites.
The reason? E-commerce sites get updated many times per month. Whether you upload new products or delete outdates ones, any changes on your site can lead to SEO errors that might hinder your search engine visibility.
I typically use Ubersuggest or SEMrush to perform my monthly SEO audits. Because I personally prefer to use Ubersuggest, let me show you the steps on how to do it there:
How to perform an SEO audit via Ubersuggest
- Login to Ubersuggest
- On the left-hand menu, click on “Site Audit”. You’ll be taken to the site audit page.
- On the space provided, enter your site’s domain name or URL
- Click on the arrow button on the right to start the audit.
- Give the tool a few minutes to crawl the site and detect any errors
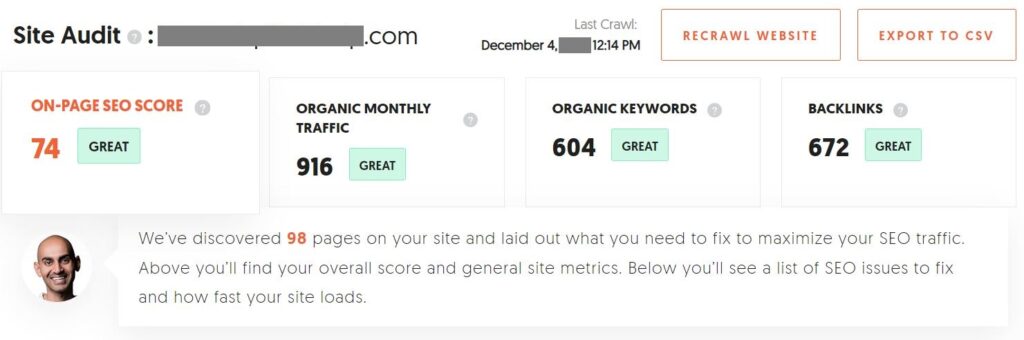
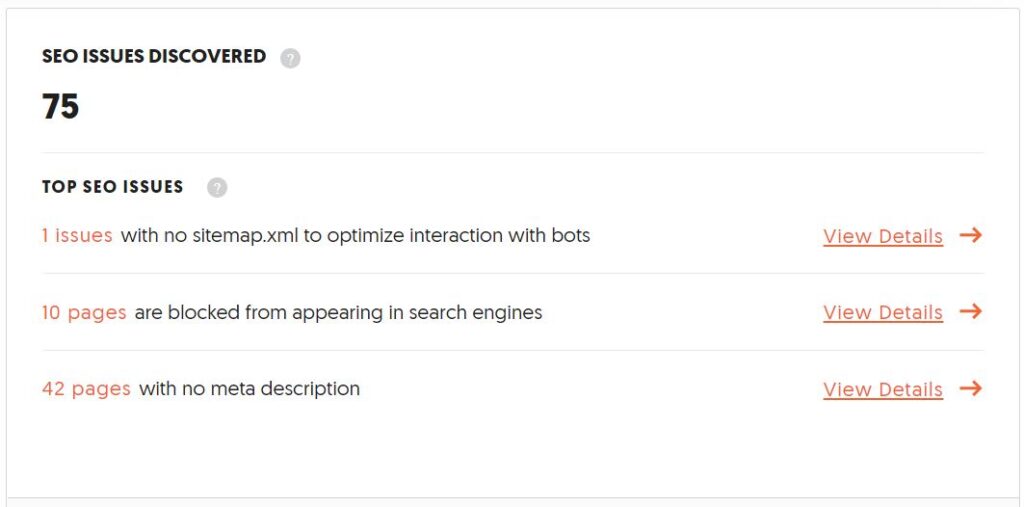
- After the crawl, scroll down and look for the section that says “SEO Issues Discovered” .
You’ll see something like this:
The process is similar whether you use SEMrush, Diib, Ahrefs, or Moz.
Based on what you see in the audit report, you may now view the details of each reported error and implement fixes on your own by researching it online.
Alternatively, you can also hire an SEO agency like Search Marketing Pad to resolve the SEO errors for you on a monthly basis. We use a variety of tools to get this job done.
Master The Common Errors Found on Ecommerce Sites
As you go fixing technical SEO issues, you’ll find that some of the errors occur regularly than others. Here are the most common ones to look out for:
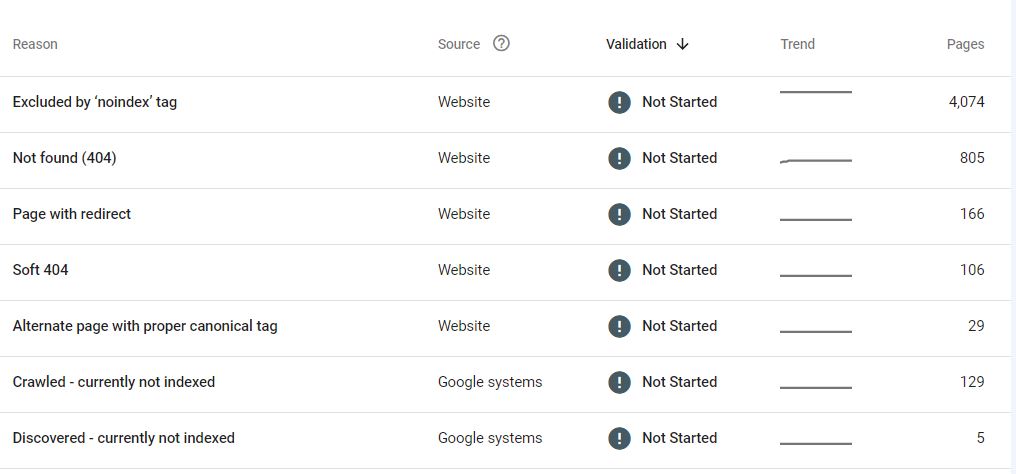
Duplicate Meta Titles and Meta Descriptions
What Is It: It means that two or more pages on your site have the same title tags or description tags.
Why You Should Fix It: Google hates any form of duplicate content. Pages with duplicate content (such as those with the same meta tags) don’t do well on search results. They could also increase the chances of a Google penalty for your site or a total disappearance from search.
Causes: The most common cause is a SINGLE page with different URL versions. Although there is only one page, Google sees it as several different pages. In e-commerce sites, this could arise from URL versions generated from dynamic product pages.
Other causes include: 1) global meta tags applied to many or all pages, 2) old page drafts that are not deleted and are still live, 3) duplicate product listings, and many others.
How To Fix It: The fix would depend on the specific cause of duplicate content, but typically involves any of the following:
- content merging
- canonical tag implementation
- 301 redirects
- noindexing and nofollowing
- a mixture of any of the above.
404 “Not Found” Errors or Broken Links

What Is It: A “404 error” usually happens when the Google spider or your web browser tries to access a webpage on your site, but doesn’t find it. Either the page is deleted/deactivated, or there are server-side problems causing it not to show.
Why You Should Fix It: A 404 “not found” error is basically a dead end page. When Google hits a 404 page, it basically can’t crawl or access the content that used be present in that page. Thus, any previous Google ranking that the 404 page used to have will be gone.
After a while, Google just removes the page from the search results. Sometimes, it could take a while for that deindexing to happen. Meanwhile, people are still seeing them on search results and the user experience on your site suffers.
Causes: The most common cause for 404 pages on an ecommerce site is deleted/deactivated product pages. Sometimes, server issues are to blame as well. If your site is on a shared hosting plan and has limited bandwidth, your pages can down as soon as you hit your monthly bandwidth limit.
How To Fix It: Prevention is better than cure. Don’t just remove pages on your site, especially those that have already been indexed by Google. When you deactivate a product page, make sure you 301 redirect it to the new product page version, or to the closest category page.
Get a higher hosting plan that can accommodate the kind of traffic that your website receives on a monthly basis.
Pages With Multiple H1 Headings
What Is It: This error happens when a single page on your site has more than one H1 tag.
Why You Should Fix It: Your H1 heading, usually seen as the main title of a post or page, is the most prominent heading that Google looks for. It provides clues to search engines as to what the content of a page is all about. Having more than one H1 heading on any page makes it difficult for Google to read your page.
Causes: It’s typically caused by GREAT web design that’s done by non-SEO people. While the fonts and layout might look awesome, some websites just don’t have proper H1 tags assigned to their pages.
How To Fix It: The key is to just go in to the CMS or website editor you’re using and apply the <h1> tag to the main heading of each of your pages.
If you’re using WordPress, the individual title of each of blog post becomes the H1 automatically. Make sure you turn it into a keyword rich but highly readable heading. Avoid creating any new H1 tags on the page or post. Change any duplicate H1 tags into H2 or H3 instead.
With the help of your web development team or an SEO expert, you can resolve these errors easily. Our SEO packages here at Search Marketing Pad include website error fixes and resolution in our monthly service bundles.
Build Links To Your E-Commerce Website
If you really want your online store to gain traction, you need to be able to build powerful, quality links to it.
Link building can be a very broad topic and can be the subject of a separate post. However, for e-commerce sites there are some good ways to build links. Here are some of them:
Unlinked Brand Mentions
Search out websites that mention your store’s brand name. Contact the webmaster of that specific website, point out the unlinked mention, and request them to add a link towards your website (from the specific phrase where they mentioned yourbrand).
In many cases, webmasters would ignore the request, but the small percentage of websites that do respond to your link request will make a great deal of difference.
Round-Up Posts
If you have lots of products on your store, create “round up” or list articles based on popular keywords. List down your best products, add a short informative blurb on each of them and add to your round up post. A typical listicle/roundup would be “27 Sun Protective Hats You Can Wear This Summer”.
Share your roundups via social media or your email lists. These types of articles, when timely and written with good quality, tend to be re-shared and linked to by lots of people.
Competitor Email Outreach
Sometimes the simplest way to build powerful links is to check your competitor’s link sources. You can perform competitor link research by using any standard enterprise SEO tool such as SEMrush, Ahrefs, Agency Analytics, and my favorite, Ubersuggest.
The idea is to find out which referring domains are linking towards your competitor’s pages. Once you have a list of these websites, reach out them via email.
Go straight to the point. Tell them that you’ve noticed they are linking to [name of competitor] from one of their blogs. Send them a link to a similar blog post on your site and suggest it as an additional resource or link they can mention on theirs.
This technique works wonders if the content you put up on your site is BETTER than your competitor’s. So always aim to produce insightful, top-notch quality, and comprehensive content that people would never hesitate to link towards.
Conclusion
So we’ve tackled some of the best SEO practices for e-commerce websites.
Though some of the techniques described sound simple, they are never easy.
It takes hard-work, grit, consistency and discipline to see results in SEO. But once you see results, the time and investment are all worth it!
Do you need an expert team to just help you manage your digital marketing and do all the SEO nitty-gritty for you? Contact Search Marketing Pad for a free consultation and quote.
